Embedded System – What is it?
Whenever I hear the term “Embedded System”,
what comes to mind is “A combination of hardware and software” as
instructed at the colleges. Well, instead of calling it as merely a
combination of hardware and software, it would be apt to define it as
application specific, organized hardware, controlled by specific
software in which the hardware and software are the components of the
embedded system. And there are many versions of the definition of an
embedded system which ultimately culminate as said above.
“Parts” of an embedded system?
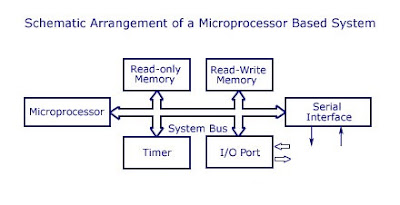
Mainly, the hardware components
constitute power source, microcontroller/microprocessor, timers, memory,
and whatever needed for running the specific task. And the software
components constitute programs such as compilers, integrated development
environments (IDE), assemblers, simulators etc., which are used to
create codes that “instruct” the hardware to do the assigned job in an
efficient manner.
Notable computer languages that are used
for programming in embedded systems are embedded C, embedded C++,
embedded JAVA and assembly. Here embedded C and others contain a
specific library for a microcontroller to work. (Like the specific
header files such as math.h, conio.h). Mostly, for simple applications,
an assembly is used, which produces more efficient, compact codes.
Some of the open-source operating systems
used in embedded systems are Android, Microcontroller operating system
(µCOS), VS works.
The secret of Processor/Controller:
Microcontroller/microprocessor is
analogous to the brain of the embedded system. It performs all the
calculation and decision part of the process. You would be surprised to
know that the only arithmetic operation the processor/controller is
capable of doing is, addition! (and the modern computer too).
Multiplication is repeated addition, subtraction is the addition of
negative numbers and division is repeated addition of negative numbers.
War at the core – processor vs. controller:
Well, we have already written a good article pointing out the basic differences between a microprocessor and microcontroller. Have a go through for better understanding.
This doesn’t mean that microprocessor is
less applicable! It is as important as the microcontroller which has its
own applications. In general, the microcontroller is designed for a
specific purpose. [For example, an automatic washing machine, a cell
phone etc. Of course, you can implement the same cell phone with a
microprocessor, but it takes too much space and also as much circuitry
is involved, more power is consumed.] But microprocessor is designed for
a general purpose. The same microprocessor can be used for designing an
automatic washing machine and also a cell phone, but that’s not the
case with microcontrollers, its specific for a specific device. In
summarizing, we can roughly refer the microcontroller as an enhanced
microprocessor, enhanced for a specific task.
Some Examples:
Many companies such as Integrated
electronics, Microchip, Atmel, Philips, Hitachi manufactures
microcontrollers. Most notable among them are, 8051 from Intel, PIC
series from Microchip, AVR series from Atmel, 68HC11 and HD44780 LCD
controller from Hitachi. The PIC controllers are mostly used by
hobbyists. Some examples of the embedded system worth mentioning are
cell phones, air conditioner, car dashboard control, PMPs, robots,
scientific calculators etc.
Applications of embedded systems
Embedded systems are used in a wide range
of industries ranging from calculators to drones. Below are certain
applications of embedded systems;
Traffic control system
Embedded system integrated traffic lights
can detect which directions have the highest density of traffic and
change the traffic lights and their timings based on this info. This
will be a great boon to cities that are controlled by fixed timer
traffic lights.
Smart homes
IOT (Internet Of Things) is closely knitted
with embedded systems. All the appliances of a smart home which can be
controlled via the internet are integrated with embedded systems.
Automotive industry
Vehicles are equipped with embedded
systems. Major functions like temperature control (AC), ABS, airbags,
automatic rain sensor wipers etc are controlled by these systems.
Healthcare
A lot of instruments used in healthcare
like blood pressure monitor, scanners, pacemakers etc works with the
help of embedded systems.
Aerospace industry
Hardly anything used in advanced engineering is without embedded systems.
The applications of embedded systems in
today’s world is in numerous. I think it is easier to give you a list of
things that don’t use them.